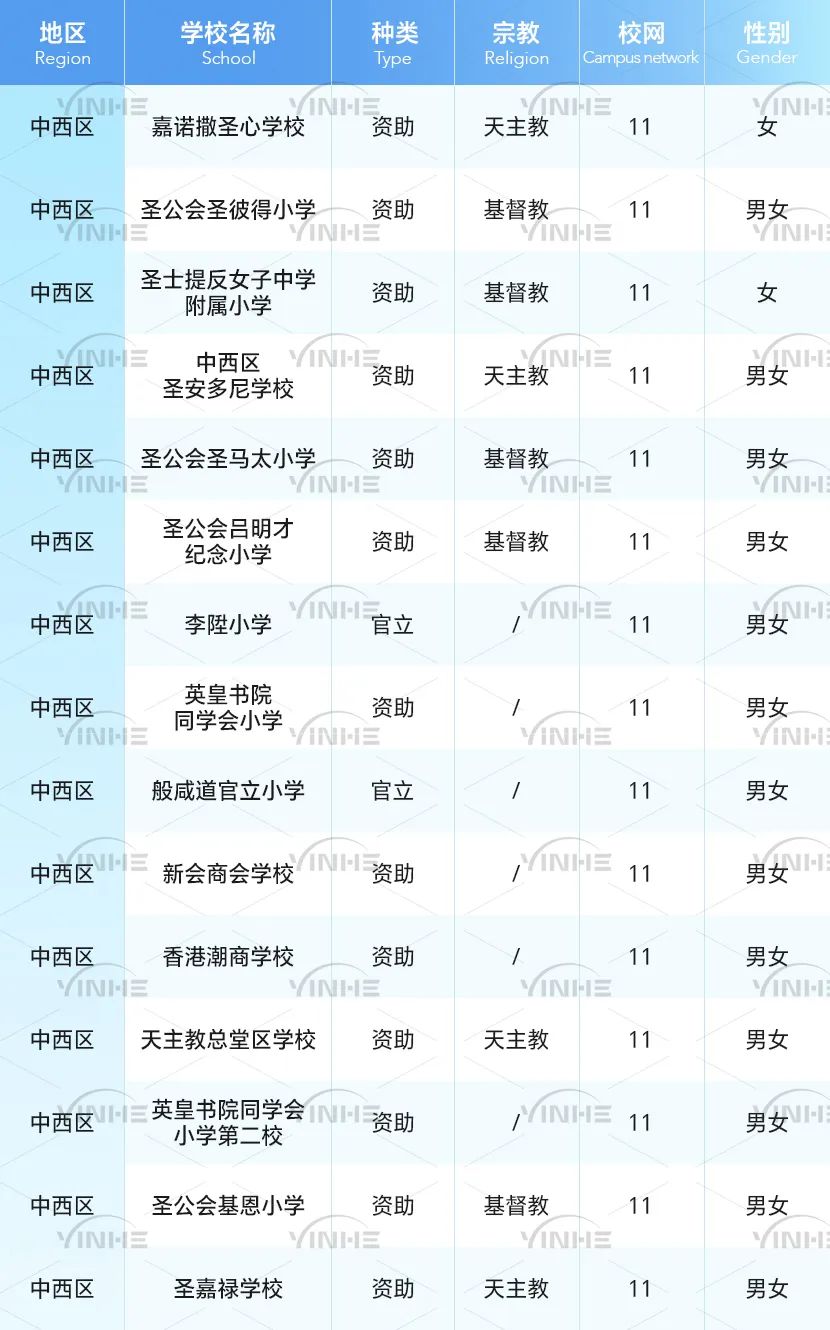
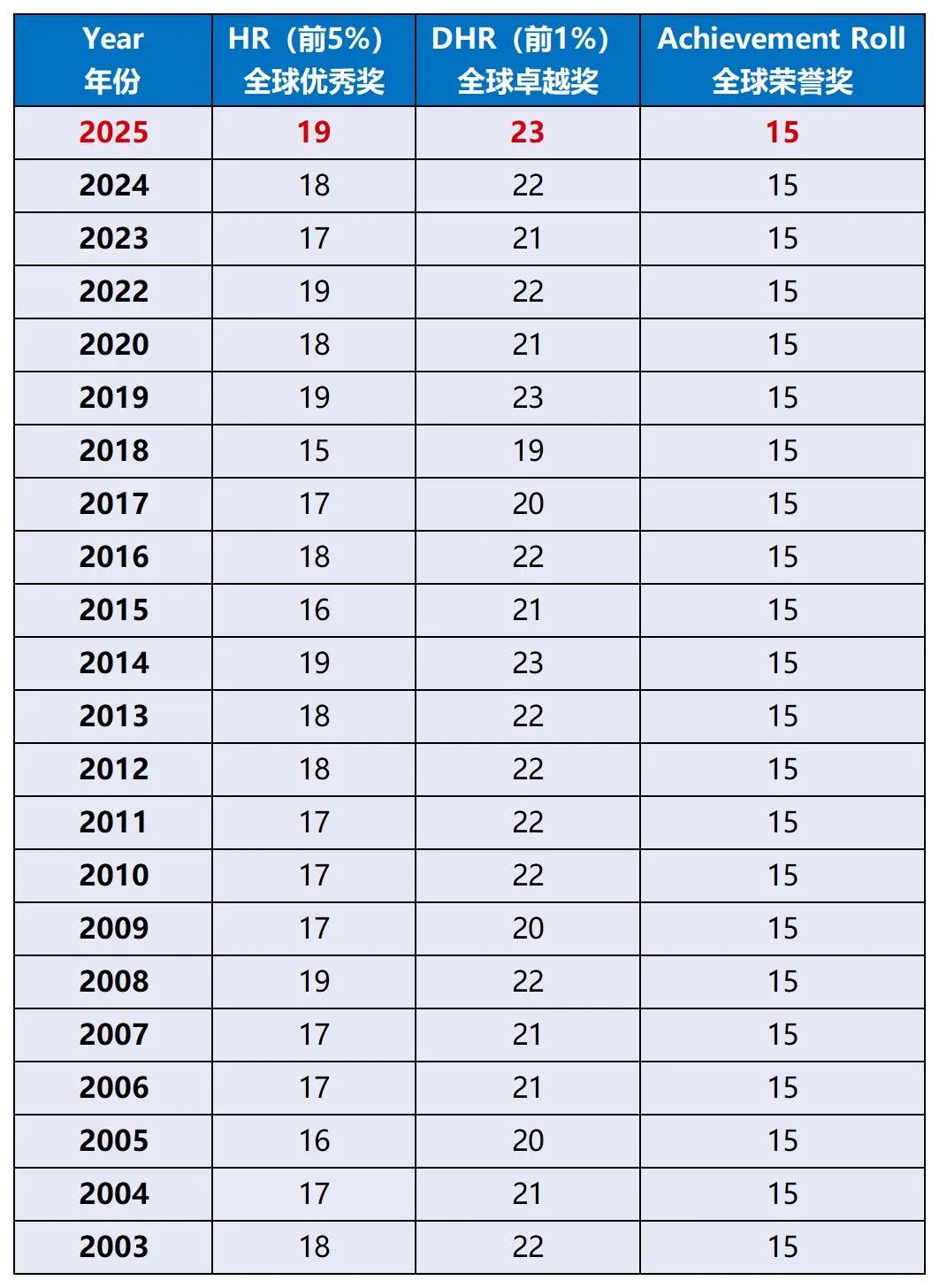
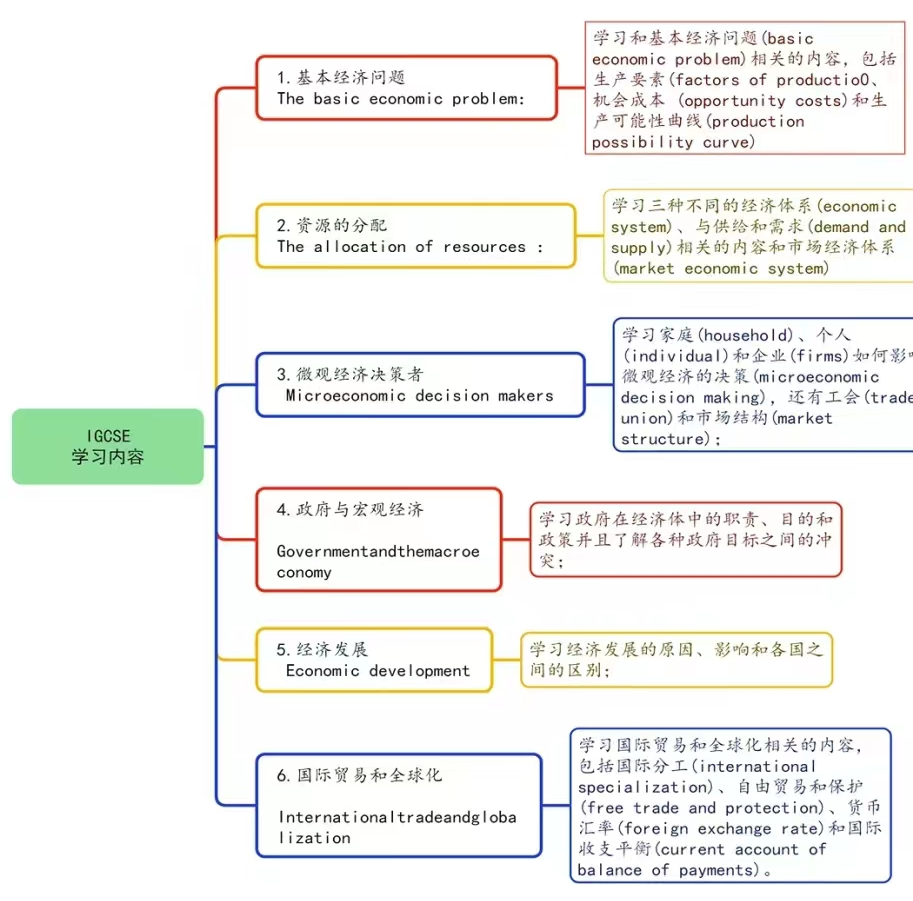
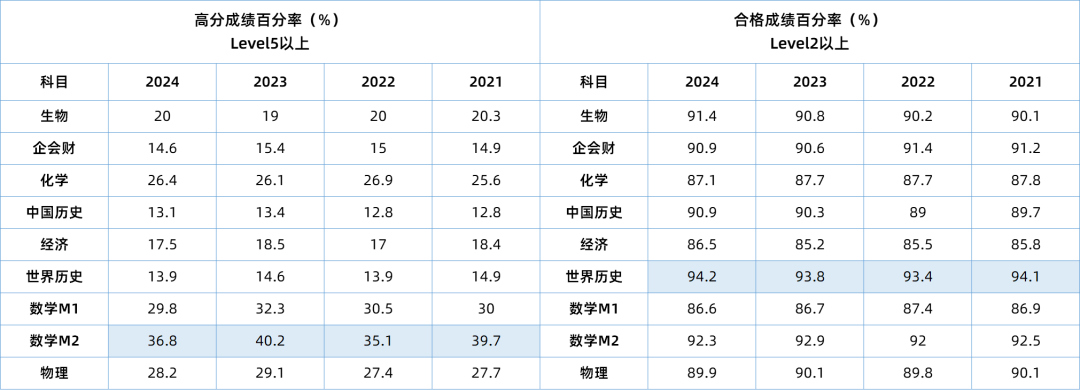
今天老师带大家爆改一篇学生的Essay。这篇文章在改动前是12分,大概B的水平。
In January 2019 the Portuguese Government announced an increase of €20 billion ofgovernment spending on transport, energy and environmental projects. It aims toimprove the productive potential of the economy.Evaluate interventionist supply-side policies as a means of achieving economic growth.(total for question=20 marks)
题目说在2019年1月,葡萄牙政府宣布了一项高达200亿欧元的财政投资计划,涵盖交通、能源和环保等领域,目标是提升国家的生产潜力,推动经济增长。那么,这类干预型供给侧政策(Interventionist Supply-Side Policies)究竟如何影响经济?它是否是实现长期增长的最佳方案?
以下是学生的Essay⬇️⬇️⬇️
Supply-side policies are mainly micro-economic policies aimed at making markets and industries operate more efficiently and contribute to a faster underlying rate of growth of real national output. Economic growth is the increase in the real value of goods and services produced as measured by the annual percentage change in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
There are two types of economic growth, one is actual economic growth which is the shift in aggregate demand, and another is potential economic growth, which is a shift in aggregate supply.
The supply-side policy aimed to shift the long-run aggregate supply curve shift to the right.
老师点评:
✅优点· 文章开头定义了supply-side policies,并简要介绍了其分类。
· 解释了economic growth,区分了实际经济增长(actual growth)和潜在经济增长(potential growth)。
❌ 需要改进的地方:
逻辑问题:
· 文章定义actual growth时错误地说是由aggregate demand shift引起的。实际经济增长的定义是“实际GDP的增长”,可以由aggregate demand (AD) 或 aggregate supply (AS) 的变化共同影响,而不仅仅是AD。
· potential growth 应该更明确地解释是由LRAS(长期总供给)向右移动导致的,而不是简单说是 AS 的变化。
There are two types of supply-side policy, one is interventionist, and another is market base. Interventionist supply-side policies are usually aimed at correcting market failure, which includes government spending on training and education, improved health care, new technology, infrastructure or transport.
Free market supply-side policies aim to increase efficiency by removing things which interfere with the free market.
They include tax cuts, privatisation, deregulation, and policies to increase labour market flexibility.
老师点评:✅优点提及了市场导向(market-based)和干预型(interventionist)供给侧政策的区别。
❌ 需要改进的地方:
1. 定义缺少深度:· 可以补充LRAS 为什么会右移(如提高生产率、增加劳动力、技术进步等)。
2. 语言表达:· “The supply-side policy aimed to shift the long-run aggregate supply curve shift to the right.” 句子结构不够流畅,应改为 "Supply-side policies aim to shift the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve to the right by improving productivity and efficiency."
💡改进后的示范句:“Economic growth refers to an increase in the productive capacity of an economy, measured by the annual percentage change in real GDP. There are two types of economic growth: actual economic growth, which occurs due to an increase in AD or SRAS, and potential economic growth, which is achieved when LRAS shifts outward due to improvements in productivity, human capital, and infrastructure. Supply-side policies aim to shift the LRAS curve to the right, increasing the economy's potential output. These policies can be classified into interventionist and market-based approaches.”
One interventionist supply-side policy might be to improve training and education. More and better training and education lead to an improvement in the quality of labour resources, increasing the productivity of labour. Public training and education programs can assist workers to become more employable, thus reducing the natural rate of unemployment. However, it takes a long time to see the results of the effects on an economy’s labour supply that occur from improvements in education, so it can not be used to fix the market quickly.
老师点评:
✅ 优点:
· 识别出了教育和培训对提高劳动力质量和降低自然失业率的作用。
· 提到了时间滞后(time lag),是一个很好的评估点。
❌ 需要改进的地方:
1. 缺乏例子和数据支持:
· 可以提供具体国家或地区的例子,例如德国的职业教育体系(dual vocational training system),或者新加坡的人才培养政策。
2. 缺乏政策局限性的分析:
· 政府财政负担(如公共教育投资的机会成本)没有提及。
· 市场失灵可能导致教育资源分配不均,例如农村地区可能无法享受同样水平的培训资源。
💡改进后的示范句:“Government investment in education and training enhances human capital, leading to higher labor productivity and reduced structural unemployment. For instance, Germany's dual vocational training system has successfully integrated students into the labor market, improving long-term economic growth. However, this policy has limitations: it requires significant government funding, and the benefits take years to materialize. Additionally, inefficient allocation of education resources may lead to regional disparities, reducing its overall effectiveness.”
Another policy might be improved health care services. When workers have access to good quality healthcare services, they become healthier and more productive.
Improved health care services by the working population, will cause them to work longer hours per week, which is, therefore, another factor leading to improvements in the quality of labour resources, which will lead to an outward shift in long-run aggregate supply. However, it cost a lot of money, which will have opportunity costs on it. For example, the government may use this money to invest in some firms, which will cause a bigger increase in GDP.
老师点评
✅ 优点:
· 识别出医疗保健可以提高劳动力质量,并使 LRAS 右移。
· 提及了机会成本的概念。
❌ 需要改进的地方:
1. 逻辑不清晰:
· 句子结构混乱,尤其是 “Improved health care services by the working population, will cause them to work longer hours per week”。
· 逻辑跳跃:未解释“健康工人→生产率提升”的具体机制(如减少病假、延长工作年限)。
2. 机会成本分析不深入:
· 讨论政府财政限制,例如是否需要提高税收来支持这一政策?
💡改进后的示范句“Investment in healthcare enhances labor productivity by reducing absenteeism and increasing life expectancy. For instance, Sweden’s universal healthcare system has led to a healthier workforce, boosting economic growth. However, such policies require significant government funding, potentially leading to higher taxes or reduced spending in other areas such as infrastructure, which could also contribute to growth.”
The next policy is to reduce the welfare for unemployment and decrease the minimum wage for labour.
By reducing the welfare for unemployment, the employee will try their best to work in the firm, in order to not be fired. Thus, this will lead to an increase in productivity, as a result, there will be an increase in aggregate supply. By decreasing the minimum wage for labour, firms will hire more labour, as the cost of labour is cheaper.
More workforce means they will produce more, which will lead to an outward shift in aggregate supply. According to the diagram, there is an outward shift in aggregate supply, the initially the macroeconomic equilibrium is at point S.
When the LRAS curve shifts from LRAS to LRAS1 as a result of the supply-side policies, the new macroeconomic equilibrium is now at point T.
And because supply-side policies aim to make firms more productive and efficient, the risk of cost-push inflation is also low. which we can see that there is a decrease in price.
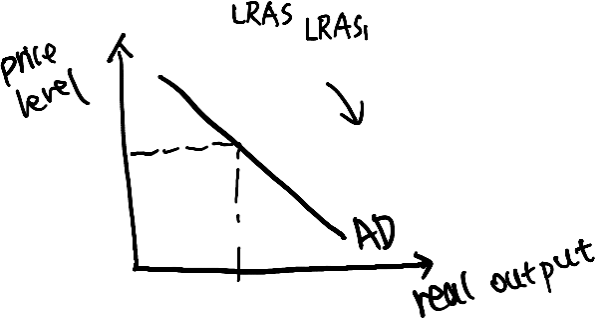
老师点评
✅ 优点:图画得很正确
❌ 需要改进的地方:
1. 缺乏对于图的解释,可以说Supply side policy shift LRAS to the right from LRAS to LRAS1,lead to increase in real GDP and lower price level
2. 概念错误:减少福利和最低工资属于market-based(非干预主义)政策,与题目要求无关。
3. 结论错误:供给侧政策虽可能降低通胀,但学生误用“cost-push inflation”解释(实际应关联LRAS右移降低价格水平)
💡改进后的示范句:"A true interventionist approach would be subsidising green energy R&D – Portugal’s environmental projects could reduce firms’ production costs via renewable energy, shifting LRAS rightward without income inequality risks from cutting welfare."
However, the benefit cuts can lead to the poorest people in society worrying about their ability to cope financially. Greater flexibility in the labour market and trade union reforms could lead to some people having less job security.In conclusion, whether interventionist supply-side policies as a means of achieving economic growth depends on whether in the short run or long run. In the short run, it is better to use market base supply-side policies because it saves time, in the long run, it is better to use interventionist supply-side policies.
老师点评
✅ 优点:
· 讨论了短期 vs 长期的对比,这是一个有价值的评估点。
❌ 需要改进的地方:
1. 结论太简单,没有足够的分析或总结主要论点。
2. 没有权衡政策之间的影响,例如是否可以混合使用两种政策
💡改进后的示范句“In the short run, market-based policies may yield faster results, but interventionist supply-side policies are essential for long-term sustainable growth. Governments must balance these approaches, considering fiscal constraints and implementation efficiency to maximize economic benefits.”
本题总结——提分关键⬇️⬇️⬇️
1. 严格区分政策类型:干预主义(政府主导) vs 市场主导(减少干预)。
2. 紧扣题目关键词:始终围绕“productive potential”和“evaluate”展开,比较不同政策优劣。
3. 数据与案例强化说服力:· 引用葡萄牙投资细节(如“60% of the €20bn is allocated to renewable energy infrastructure”)。· 对比其他国家案例(如德国职业教育体系对生产率的影响)。
4. 最终评估框架:· 短期vs长期效果· 效率vs公平性· 机会成本(如基建投资 vs 减税刺激私人部门)