国际考在即,今天给大家分享一下AS化学国际考当中的重难点!文章干货内容满满,包含——考试最新变化、三部分内容的详细解读建议诸位考生仔细阅读!
注意点1、Data booklet
Data booklet不会继续作为考题的附件提供给学生,考题中需要用到的数据会在相应的题目提供,为大家节省了在考试中查找数据的时间。
注意点2、Command words
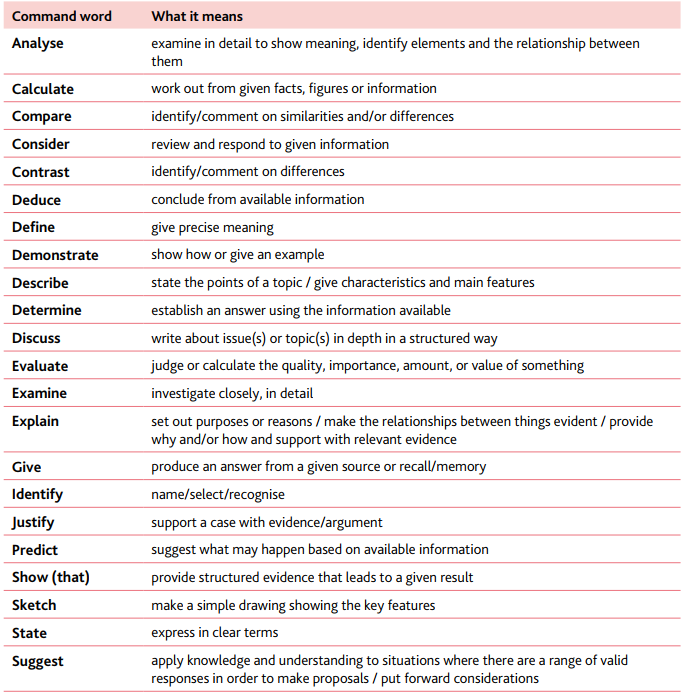
Command words
- demonstrate只需要举例
- define需要给出明确的定义
- sketch需要作图
- state需要用简短的语言做出说明
- suggest做出推测
- identify一般是指写出名字
AS化学国际考内容
International exam content
Part 1、Atomic structure and ionization energy
历年必考内容当中,今年肯定也会考的内容包括atomic structure。
这种题一般要求学生能够算出subatomic particle的数量,比如proton number, neutron number, nucleon number。
稍微难点的题目会让学生define the isotopic mass, the atomic mass, the molecular and formula mass。
与之相关的内容有比较atomic radius和ionization energy。
这两部分内容考法的相同点是across a period and down a group的比较当中都会要求学生以proton number, shielding effect, electron shell number and distance to the nucleus为基础进行讨论,比如:
- why is the ionization energy of argon much higher than that of chlorine?注意这里不须要讨论full shell。
- Which ion has larger radius, Cl- or S2-? 这里需要说明shielding几乎没有差别。
在atomic structure相关的考题当中,有一类稍微难点的题目是判断unpaired electrons in an atom,这类型的题目通常会以前三十个元素为基础,大家要会判断electronic configuration;
Cr是前三十个元素当中unpaired electrons最多的元素,Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn的unpaired electron number依次是6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1。
另外,还需要注意的是electronic configuration of period 4 transition element ions,这里4s轨道能量确实是低于3d轨道的,但是Mn2+的electronic configuration只能写成1s22s22p63s23p63d5(4s电子先于3d电子失去)。
在ionization energy相关的考题中,还需要注意的是一个常见的3分考题:define ionization energy。
此外,还需要注意如何使用shielding effect和spin-pair repulsion来解释the exceptions in ionization energy variation trend across a period(examples include comparing Mg and Al, comparing P and S)。
最后,题目中可能会给出一系列ionization energy 的数据让大家判断group number。
备考的时候不要去操心electron affinity,但是ionization energy和electronegativity的区别一定要注意。
Part 2 Substance structure and bonding
在substance structure and bonding相关部分的考题中,compare melting points of different substances是历年考试热点。
这种题型整体上呈现“三英战吕布”的格局:
那就是让大家解释为什么“giant ionic, giant covalent and giant metallic”的物质熔点要高于”simple molecular“的物质,这种体型需要同学们根据types of particles, relative strength of attraction force来做答,不需要具体深入地讨论IMF;
当题目当中要求比较两个”simple molecular“的物质时,hydrogen bonding, pd-pd force, number of electrons, surface of molecules,以这些知识点为基础具体讨论IMF就成了答题得分点。
说到bonding,AS chemistry的考试当中一般会涉及molecule shape, bond angle and hybridization。
这里要注意NH3是trigonal pyramidal不是tetrahedral;Al2Cl6和NH4+中都有dative covalent bond。
画出hybridized atomic orbital,并且合理地overlap来解释the formation of sigma and pi bond也是大家需要掌握的。
Part 3 Chemistry calculation
相比于IG考试当中的计算amount of substance,AS考试并不会在这类题目上设置很多计算题,因此以pV = nRT的题目只需要少量练习一些,但是对于why real gases are different from ideal gas的解释一定要记在心中。
在pressure很大的时候需要讨论volume of gaseous molecules and their IMF;在temperature很低的时候只需要IMF。
AS chemistry当中,计算oxidation number可以出比较难的题目,KMnO4和K2Cr2O7这两个物质是历年“分数刺客”,被它们偷袭的学生数不胜数。
Reaction rate一般会结合diagram of amount vs time来考察学生,会让大家计算reaction rate,但是这类题目都很简单;
结合Boltzmann distribution和collision theory来解释temperature, catalyst, pressure, concentration对reaction rate的影响,这些算是中等难度的题目;
结合starting amount of reactants and equilibrium constant来让学生计算Kc and Kp,这种题型肯定会作为压轴计算题考,而且多半是考Kp。
pH, Kw, Ka or pKa这些不会出现在AS chemistry的考试中。
在energetics方面,ΔHat, ΔHsol, ΔHhyd这些都不在AS chemistry的考察范围内, ΔHf, ΔHc,和bond energy这些大概率会以organic molecule为基础出题,这里要注意ΔHf是指生成1 mol compound from its elements,ΔHc是指completely combust 1 mol of compound with oxygen;bond energy是指breaking or forming 1 mol of bond。
因此在计算时一定要注意number of moles。
传统无机化学的题目一般会以group 2和group 7为主,以period 3为次。
Group 2的考试范围
Group 2的考试范围多集中在solubility of hydroxides and sulfates以及thermal decomposition of nitrates上。
在这个部分我们需要知道Mg(OH)2是溶于热水的,Mg与steam反应生成MgO而不是Mg(OH)2。
另外,group I metal and group II metal nitrates的热分解反应方程式完全不同,这个题目只要出现,就像守关boss一样会收割80%以上学生的分数。
Group 7的考试重点
Group 7的考试重点是chemical equation。
Halogen displacement, disproportionation reaction of chlorine in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, redox reaction between hydrogen halide and conc. sulfuric acid。
当然,出题方向也可能是根据carbon-halogen bond energy来判断有机反应的速度。
Period 3
Period 3只需要注意melting points of period 3 elements,以及the hydrolysis of period 3 element chlorides。
今年非常有可能考的重点是environmental issues caused by nitrogen oxides。Nitrogen oxides会以两种方式形成酸雨,第一种是直接生成nitric acid,第二种是催化SO2转变成sulfuric acid。
除此之外,photochemical smog caused nitrogen oxides也需要大家格外注意。
Organic chemistry知识体系当中,alkene, halogenalkane and alcohol这三种homologous series是绝对的核心。
Alkene
Alkene由于具有carbon-carbon double bond这种electron-rich的结构,所以它的化学性质都是围绕着electron-donating property展开的。在AS chemistry中主要体现为两类反应:
- 第一种是oxidation reaction with acidified KMnO4, 这种反应在不同温度下会有不同的氧化产物;
- 第二种是electrophilic addition reaction,亲电试剂包括bromine, hydrogen halide, and all kinds of dipole-equivalent reagents都是非常好的考试素材。这里electrophilic addition mechanism是大家一定要掌握的。
Halogenalkane
Halogenalkane由于具有疏水性,所以一般不用水作为溶剂,而是用ethanol作为溶剂,在答题的时候一定要注明ethanolic。
Halogenalkane具有carbon-halogen bond,这种化学键由于其良好的polarity,可以很容易地发生nucleophilic substitution reaction。
SN1 and 反应机理都需要大家熟练掌握,dipole sign with partial charge, lone pair and position of starting point and end point of curved arrow是三个常见的丢分点。
这里还隐藏着一个阴险的丢分陷阱,那就是ethanolic NaOH不能使halogenalkane发生取代反应,而是发生消除反应。(这个消除反应的机理是不用掌握的)
Alcohol
Alcohol的化学性质主要体现在三种不同的类型的反应当中。
第一类反应
第一类反应为redox reaction,acidified KMnO4 and K2Cr2O7都可以使它发生氧化,但是又分为reflux和distillation两种不同的情况。
在Distillation的条件下,aldehyde and ketone是氧化产物,这些carbonyl compound的identification using 2,4-DNPH, alkaline I2, Fehling’s reagent and Tollen’s reagent都是几乎必考的内容。
在reflux的条件下,ketone or carboxylic acid是主要产物。
第二类反应
第二类反应为substitution reaction,这是alcohol转化为halogenalkane的反应,它本质上也是SN反应,但是反应机理大家不必深究,只需要掌握如PCl5和SOCl2之类的试剂就行。
第三类反应
第三类反应为elimination,这是alcohol转化为alkene的反应,同样不需要大家掌握反应机理。
除此之外,reduction of carbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids,hydrolysis of esters and nitriles这两类反应也需要大家了解。
IR部分需要大家掌握如何区分carboxyl and hydroxyl group,如何判断the presence of carbon-hydrogen bond,但是C=C和C=O这两种化学键不需要区分。